MENU
Global Standards Package
The Global Standards Council
Interoperability, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness are cornerstones for evolving technologies in justice information sharing. The Global Standards Council (GSC) stands as a gatekeeper to ensure that technical products developed in the national justice community evolve in a cohesive manner so that consumers find a single set of products that are known to work well together and reinforce one another.
The GSC’s mission is to coordinate the broad-scale electronic sharing of pertinent justice and public safety-related information by coordinating the establishment of a common, consistent, and standards-based approach to implementing justice information sharing solutions. The GSC is responsible for the development and maintenance of normative information sharing technical exchange standards, including proposed standards submitted by consumers and stakeholders. For more information on the GSC, please visit the Global Standards Council page.
The Global Standards Package
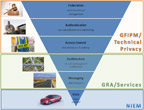
To achieve the interoperability and cost-saving aims of the GSC, the Global Standards Package (GSP) was developed. The GSP is a collection of normative, independently versioned standards that are assembled into a package of composable, interoperable solutions specifically supporting the exchange of justice information.
GSP solutions are generally technically focused but also may incorporate associated guidelines and operating documents that include instruction and education, policy recommendations, and tools and templates. GSP deliverables also include artifacts associated with many of the Global product areas, including topics centered on Data, Messaging, Architecture, Access Control, Authentication, and Federation Management.
Components of the GSP
The GSP is composed of the following primary components:
National Information Exchange Model (NIEM)
NIEM helps to eliminate confusion associated with different data definitions across law enforcement and public organizations by providing a common vocabulary to ensure consistency and understanding among state, federal, and local agencies. For more information on NIEM, please visit https://www.niem.gov/.
Global Reference Architecture (GRA)
The GRA offers guidance on the design, specification, and implementation of services and related infrastructure for organizations that are looking for an architectural solution to sharing information through external exchanges and common messaging standards between information sharing systems. For more on the GRA, including access to free online training, visit bja.ojp.gov/program/it/national-initiatives/gra.
Global Service Specification Packages (SSPs)
Reference services that serve as the means by which the information needs of a consumer are connected with the information capabilities of an information provider. Developers, architects, and service authors are strongly encouraged to refer to the following namespace site when developing Global service specifications. This namespace provides a collection of names, identified by uniform resource identifiers (URIs), which are used to support GRA service specifications, service specification artifacts, packaging metadata, and sample documents.
Global Federated Identity and Privilege Management (GFIPM)
The GFIPM specifications and guidelines are designed to support security controls when accessing justice information systems, based on commonly understood and applied user access control policies.
Global Privacy Technology Framework
The technical privacy framework is a methodology and series of tools designed to support defining the data privacy and confidentiality rules and disclosure obligations based on various roles and conditions.
Importance of Global Standards Package Implementation
The use of these standards is important to lower overall acquisition costs by leveraging the economies of scale inherent within local, state, tribal, and federal governments while enhancing data sharing and system integration across agencies. Associated benefits of using the aforementioned standards include the following:
| Interoperability | Life Cycle Costs |
|
|
Global Standards Package Compliance for Grant Funding
To promote increased interoperability among justice information sharing systems, the Office of Justice Programs (OJP) has started issuing guidance relative to the use of the GSP. Specifically, the OJP assigns the following conditions to grant and cooperative agreement funds supporting the exchange of justice information:
"In order to promote information sharing and enable interoperability among disparate systems across the justice and public safety community, OJP requires the grantee to comply with DOJ’s Global Justice Information Sharing Initiative (DOJ’s Global) guidelines and recommendations for this particular grant. The grantee shall conform to the Global Standards Package (GSP) and all constituent elements, where applicable, as described at: bja.ojp.gov/program/it/gsp-grant-condition.
The grantee shall document planned approaches to information sharing and describe compliance to the GSP and appropriate privacy policy that protects shared information, or provides detailed justification for why an alternative approach is recommended.”
Compliance with the GSP requires conformance to all components of the GSP whenever applicable.
- If the grantee is planning to exchange information across agencies or systems using a common data format, such format is required to be conformant to the NIEM.
- If the grantee is planning to adopt a service-oriented approach to sharing information, it must leverage the GRA, and so on.
- If the grantee is planning to establish a single-user identity and privilege system across domains, the Global Federated Identity and Privilege Management method should.